
In technical use the term is avoided because of ambiguity with boxes.

In addition, groups of clues can display other types of symmetry, such as translational symmetry. reflection symmetry on two diagonal axes.reflection symmetry on one diagonal axis.reflection symmetry on two orthogonal axes.reflection symmetry on one orthogonal axis.Symmetry – A Sudoku can have seven types of overall symmetry in its clue positions.Translational symmetry (each clue group takes the form n, n+1, n+2, n+3), (24 clues). Size – Refers to the size of a puzzle or grid, and can be described as a composite (i.e.
#NISHIO SUDOKU STRATEGY TRIAL#
Note: the level of trial and error is usually not explicitly defined.

In some variants regions are not equally shaped. Region – Another term for the boxes of a Sudoku.Sudokus are always expected to be proper Sudokus unless the puzzle setter specifies otherwise. Proper Sudoku – A Sudoku with one solution.In some variants nonets are not equally shaped. Nonet – Another term for the boxes or regions of a Sudoku.(See Mathematics of Sudoku – Minimum number of givens for details). Minimum number of clues – Refers to the minimum of all proper Sudokus.Different minimal Sudokus can have a different number of clues. Minimal – A minimal Sudoku (or irreducible Sudoku) is a Sudoku from which no clue can be removed leaving it a proper Sudoku (has one solution).Latin square – A related puzzle, or number array, with only row and column constraints (omitting the box constraint).In large Sudokus, such as "Sudoku the Giant", elements may be alphanumeric, or a larger set of numbers, e.g. This term is often used in a mathematical context, especially for Sudokus larger than 9×9, when more than nine digits "1-9" are required. Element – A digit or number of the Sudoku.Constraints – The rules of a Sudoku that require each digit to appear only once in each row, column, and box.In solving most Sudokus, this is usually a poor approach, but in the most difficult examples may be necessary. backtracking) and making a different guess.
#NISHIO SUDOKU STRATEGY MANUAL#
In the manual form, it indicates the effort of making a guess, and if found to be wrong, going back (i.e.
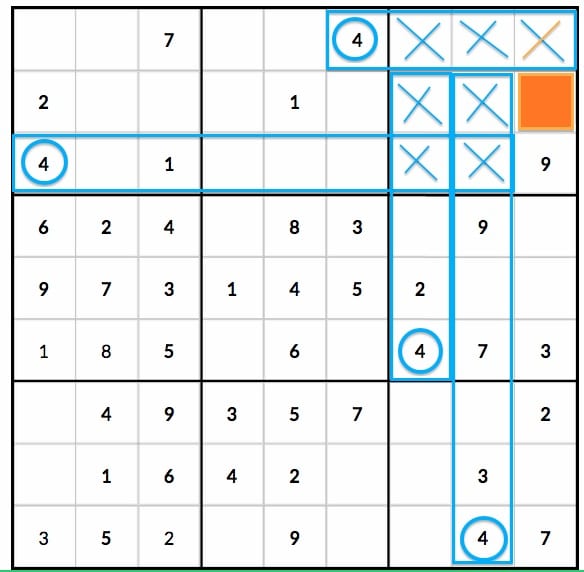
These 4 positions are coupled together, forcing an additional elimination. I don't have any other name for it, but the way I see it You can see here, regardless of whether you put 4 or an 8 in r2c1, r3c5 will be the other, which means (without guessing) you know r3c3 cannot be a 4. You find couples of pointing pairs that are linked together in a set of 4, which regardless of which number is placed in it can also eliminate candidates. For those unaware of what "pointing pairs" are (like I was, even though I used the method) here's a link to information on that.
#NISHIO SUDOKU STRATEGY UPDATE#
So I'll update the rest of the answer from here to explain what I did in addition. Others have pointed out the correct start point but not linked it to a method.Īfter comment and further review I see that my method is just an extension of pointing pairs, which was already employed on the puzzle.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
